
The simulation results show that the proposed clustering, cluster-head selection, and communications protocol design outperform the others in energy saving and significantly prolong the lifetimes of both individual nodes and the whole M2M network.

While inter-cluster communications use conventional cellular access schemes, we develop an energy-efficient and load-adaptive multiple access scheme, called n-phase CSMA/CA, which provides a tunable tradeoff between energy efficiency, delay, and spectral efficiency of the network. We further investigate communications protocols for both intra- and inter-cluster communications. T.: E-MAC: energy efficient medium access for massive M2M communications. Zander of KTH) IEEE VTC 2012-Fall, Quebec, CA, Sep. Cross-layer design for spectrum- and energy-efficient wireless networks (with J. Li of Gatech) IEEE Globecom 2012, CA, USA, Dec. Furthermore, we find feasible regions where clustering is beneficial in enhancing network lifetime. Joint PHY-MAC Design for Spectral- and Energy-Efficient Wireless Networks, (with Prof. Second, we find the cluster size to maximize the network lifetime and develop an energy-efficient cluster-head selection scheme. First, we present an accurate energy consumption model that considers both static and dynamic energy consumptions, and utilize this model to derive the network lifetime.
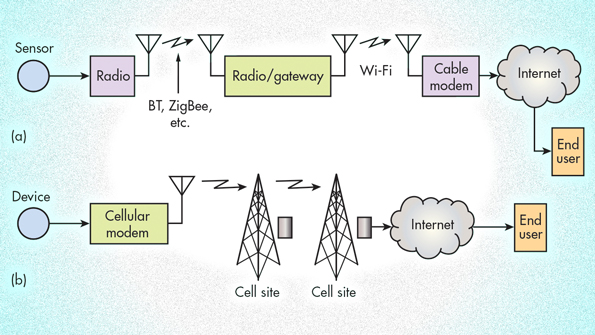
In this paper, we investigate energy-efficient clustering and medium access control (MAC) for cellular-based M2M networks to minimize device energy consumption and prolong network battery lifetime.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
